Idea to Explore
What is it like living without sight?
Discover
The pupils started by putting on blindfolds on the playground. Once everyone was blindfolded, they thought about how to do the things they normally did in the morning:
- Get to the classroom (with their own backpack)
- Take off their coat and hang it on the wall
- Find their own seat
- Take out their materials

Define
During the first activity, the pupils encountered various problems. These were discussed in the classroom.
Develop
In groups, the pupils tried to find a solution for one of the problems they encountered. They could also solve another problem they could think of.
Step 1: design: The pupils draw what they’ll build, clearly labelling the materials they’ll use.
Step 2: build: Using the materials provided they built a functional prototype that helped to solve the problem.
Deliver
A visually impaired person came to the classroom explaining what it’s like to live daily life without eyesight.
- The pupils tried on glasses emulating a certain visual impairment
- The pupils asked questions they had thought of in advance
- The visitor tried the prototypes and gave feedback and made some suggestions
- The visitor also showed what technology already offers (for example a colour-detector, screen-reading software, talking powerpoint slides…)
Pupils explored examples of how technology is helping the blind:
- Be My Eyes free app – connects visually impaired users with sighted volunteers in real time
- Seeing AI free app – describes people, text and objects and scenes. You can even get an estimate of people’s age, gender, and emotions.
- iPad accessibility options for vision
- Orcam MyEye glasses with headphones – reads aloud from any surface, recognises products, faces, money, clocks and colours.
- Aira app and headset with camera – connects blind people via augmented reality to a trained professional who can guide them as they walk around.
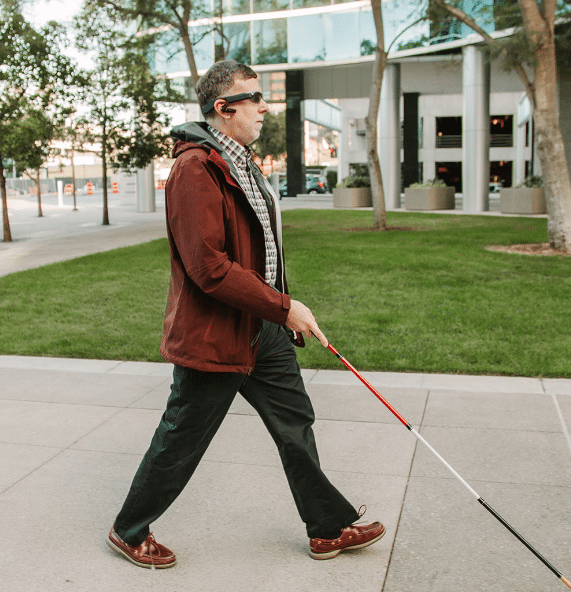
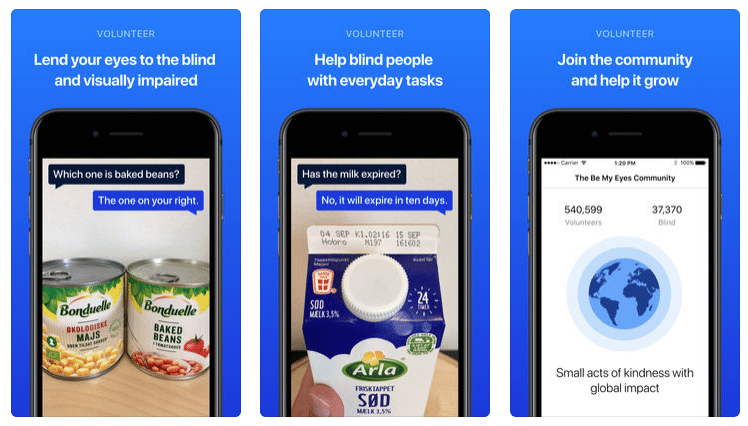

Aira app and headset with camera
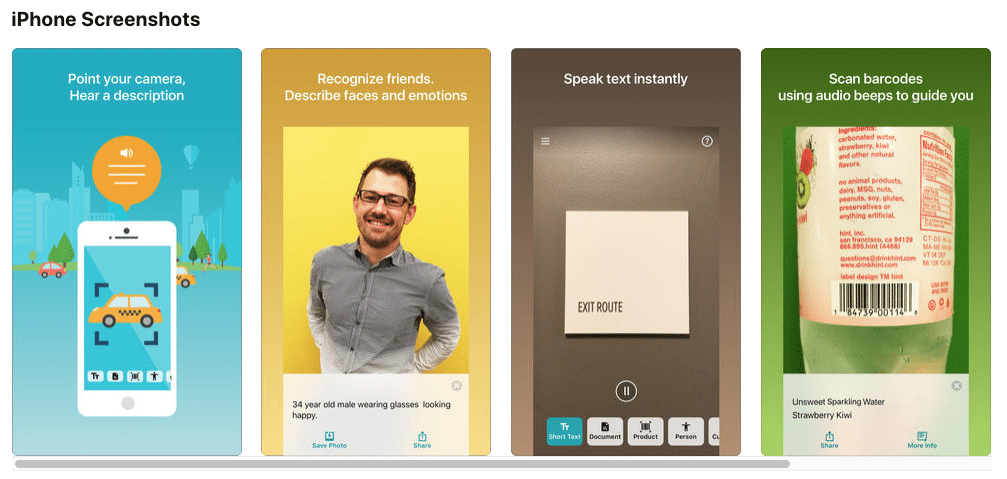 Seeing AI app
Seeing AI app
International Collaboration
The pupils shared their prototypes on a common platform, eTwinning.
Resources
- Blindfolds
- Materials to prototype with
- A visually impaired person (ideally with some of the tools they use in everyday life)
- Examples of how technology is helping the blind:
- Be My Eyes free app – connects visually impaired users with sighted volunteers in real time
- Orcam MyEye glasses with headphones – reads aloud from any surface, recognises products, faces, money, clocks and colours.
- Aira app and headset with camera – connects blind people via augmented reality to a trained professional who can guide them as they walk around.
- Seeing AI free app – describes people, text and objects and scenes. You can even get an estimate of people’s age, gender, and emotions.
- iPad accessibility options for vision
STEM to STEAM Analysis
Science: How do senses work, in particular our eyes? What causes sensory diseases?
Technology: How do visually impaired people use technology?
Engineering: Solving a problem for visually impaired people → prototyping
Art: How do blind people perceive art?
Mathematics: Construction techniques used in building prototype assistive devices for the visually impaired.
